Glucose Monitoring Watches: Revolutionizing Health Tech!
In the ever-evolving landscape of health technology, one innovation stands out as a potential game-changer: glucose monitoring watches. These sleek, wearable devices promise to make diabetes management more convenient, less invasive, and more integrated into daily life than ever before. As millions of people worldwide grapple with diabetes and other glucose-related health conditions, glucose monitoring watches are poised to transform how we understand and control our health.

Understanding the Need: A Global Health Challenge
Diabetes affects over 537 million adults globally, according to the International Diabetes Federation. This number is projected to rise significantly in the coming decades. People with diabetes must regularly monitor their blood sugar levels to avoid dangerous spikes or drops, which can lead to complications such as heart disease, kidney failure, nerve damage, and vision problems.
Traditional blood glucose monitoring methods involve finger-prick tests multiple times a day—a painful and often inconvenient task. While Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs) like those from Dexcom or Abbott’s FreeStyle Libre have already improved the landscape by offering real-time readings via sensors placed under the skin, they still involve some level of invasiveness and require separate hardware.
This is where glucose monitoring watches come into play, offering a less invasive, seamless, and potentially non-invasive way to keep track of glucose levels.

What Are Glucose Monitoring Watches?
Glucose monitoring watches are wearable devices designed to measure blood sugar levels continuously or on demand. Many of these watches resemble smartwatches like the Apple Watch or Fitbit but come with additional biosensors to track glucose concentrations.
Some models use non-invasive technologies—such as optical sensors, electromagnetic waves, or spectroscopy—to analyze glucose levels through the skin. Others still require integration with small subdermal sensors but display results directly on the watch face, improving convenience.
These watches offer:
-
Real-time glucose tracking
-
Data syncing with smartphones or cloud platforms
-
Alerts and notifications for abnormal readings
-
Integration with fitness and diet tracking apps

The Technology Behind It
Creating a glucose monitoring watch is no easy feat. Glucose is a molecule found in interstitial fluid and blood, and accurately measuring its levels without a blood sample is a major challenge. To tackle this, developers are using a variety of cutting-edge technologies:
-
Raman Spectroscopy
This technique uses light scattering to analyze chemical compositions in the skin and identify glucose levels without puncturing the skin. -
Electromagnetic Sensing
Electromagnetic sensors measure changes in tissue dielectric properties caused by glucose concentration. -
Optical Sensors
Infrared or near-infrared sensors can sometimes detect glucose molecules through the skin by analyzing the light absorption patterns. -
Fluorescence Technology
A skin patch activated by a watch emits fluorescence that changes based on glucose levels, offering indirect but accurate data.
Many leading tech companies and startups are investing heavily in perfecting these technologies to ensure medical-grade accuracy.
Market Players and Innovations
Several companies are in the race to release or improve glucose monitoring watches:
-
Apple: Rumors and reports suggest that Apple is developing a non-invasive glucose monitoring feature for future Apple Watch models, using optical sensors.
-
Samsung: Samsung has also been researching non-invasive glucose tracking, potentially using Raman spectroscopy in its upcoming Galaxy Watch lines.
-
K’Watch Glucose by PKvitality: This French biotech company is developing a smartwatch with a tiny, painless microneedle patch that reads glucose levels through the skin.
-
Afon Technology: Based in the UK, Afon claims to be close to releasing a fully non-invasive glucose monitoring watch, with results validated by clinical trials.
-
Fitbit (owned by Google): While not yet offering glucose monitoring, Fitbit’s extensive health tracking ecosystem makes it a likely contender in future developments.
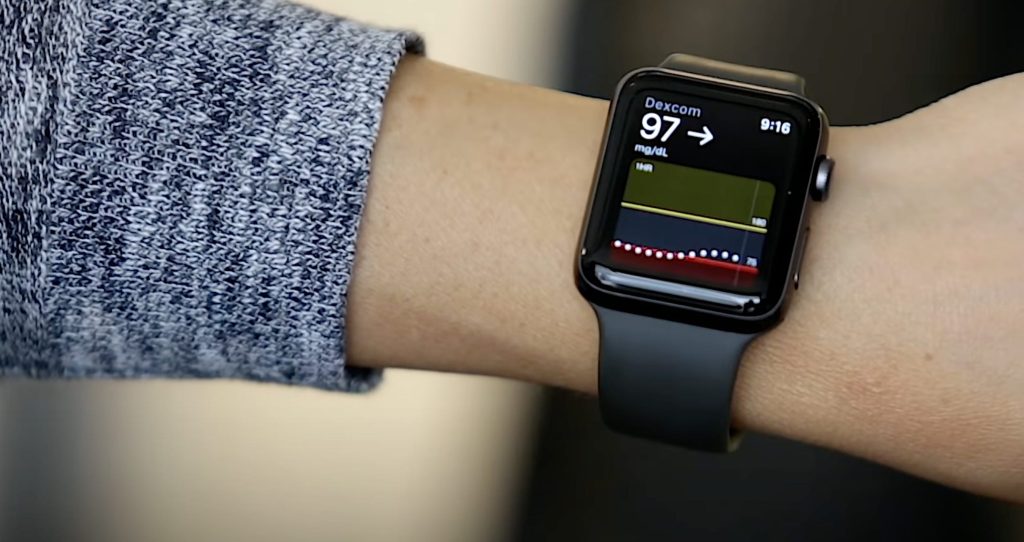

Benefits for Users
The promise of glucose monitoring watches is not just in the tech—they offer real, practical benefits for users:
1. Improved Convenience
With readings available on the wrist, users can check their glucose levels discreetly and instantly—no more carrying test strips, lancets, or bulky readers.
2. Greater Compliance
By reducing the discomfort and hassle of traditional methods, users are more likely to regularly monitor their levels, leading to better long-term control.
3. Real-Time Alerts
Glucose watches can send real-time alerts when levels rise too high or drop too low, potentially preventing dangerous hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia episodes.
4. Data-Driven Insights
Most of these watches sync with apps that allow users and doctors to track glucose trends over time, making it easier to spot patterns and adjust treatment or lifestyle.
5. Integration with Lifestyle Data
By combining glucose data with exercise, sleep, and diet metrics, users can better understand how their lifestyle choices impact their glucose levels.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite their potential, glucose monitoring watches still face several challenges:
-
Accuracy: Achieving medical-grade accuracy, especially with non-invasive methods, remains difficult and requires extensive clinical testing.
-
Regulatory Approval: These devices must receive approval from health authorities like the FDA or EMA, which involves rigorous trials and time-consuming processes.
-
Battery Life and Sensor Sensitivity: Constant monitoring can drain the device’s battery, and sensors must be both sensitive and durable over time.
-
Cost: These advanced devices may come with a higher price tag, especially during early adoption phases.
-
Privacy Concerns: As with any health tech, ensuring that user data is securely stored and not misused is crucial.
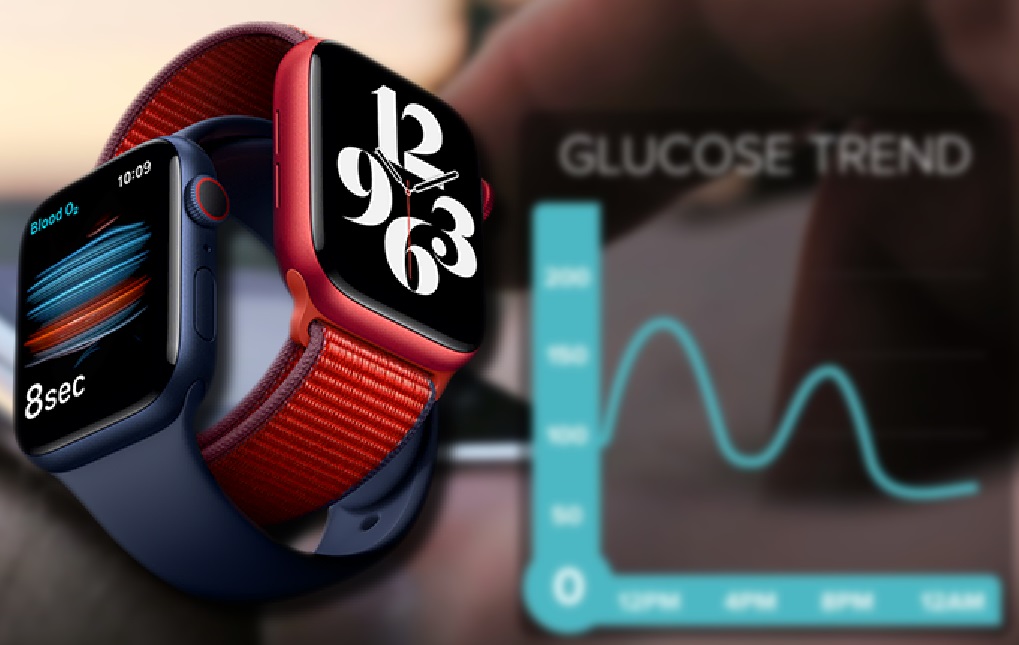
The Future of Glucose Monitoring Watches
The road ahead is promising. Experts believe that within the next few years, non-invasive glucose monitoring will become a standard feature in high-end smartwatches, much like heart rate or blood oxygen tracking. This development could have profound effects—not just for people with diabetes, but for anyone interested in optimizing their metabolic health.
In fact, as metabolic health becomes a growing concern globally, more people may use these devices proactively to monitor how their bodies react to different foods, activities, and stress levels. This could spark a new wave of health awareness and lifestyle change, supported by real-time data and AI-driven insights.
Imagine receiving a gentle vibration on your wrist telling you that your blood sugar is dropping, just in time for a snack before a workout. Or seeing how your glucose spikes after certain meals and adjusting your diet accordingly. Glucose monitoring watches may soon make this a reality.
Conclusion
Glucose monitoring watches represent a significant leap forward in personalized healthcare and wearable technology. By offering continuous, often non-invasive glucose tracking, these innovative devices empower users to take charge of their health like never before. While challenges remain, ongoing research and technological advances are rapidly closing the gap between ambition and reality.
As this technology matures, it has the potential not only to improve the quality of life for millions living with diabetes but also to become an essential tool for broader health and wellness. The future of health tech is not just wearable—it’s watchable, trackable, and deeply personal.









