Common Cures for Arthritis Pain
Arthritis is one of the most prevalent chronic conditions worldwide, affecting over 350 million people. It encompasses more than 100 different types of joint diseases, the most common being osteoarthritis (OA) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA). While arthritis is often associated with aging, it can affect individuals of all ages. The good news is, there are numerous treatments available—both natural and medical—that can help reduce inflammation, relieve pain, and improve joint function.
In this article, we’ll explore the most common and effective cures and treatments for arthritis pain, ranging from medications and physical therapy to lifestyle changes and alternative remedies.
1. Medications
Pharmaceutical intervention is often the first line of defense against arthritis pain. Depending on the type and severity of arthritis, a doctor may recommend one or more of the following:
a. Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
NSAIDs like ibuprofen (Advil) and naproxen (Aleve) are widely used to manage arthritis symptoms. They work by reducing inflammation, which in turn helps relieve pain. However, long-term use can lead to gastrointestinal issues and other side effects, so it’s important to use them under medical supervision.
b. Analgesics
Unlike NSAIDs, analgesics such as acetaminophen (Tylenol) relieve pain without reducing inflammation. These are often used for mild to moderate arthritis pain, especially in people who cannot take NSAIDs.
c. Corticosteroids
Corticosteroids like prednisone can be taken orally or injected directly into the affected joint to rapidly reduce inflammation. These are typically prescribed for severe flare-ups but are not a long-term solution due to potential side effects like bone loss and immune suppression.
d. Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs)
For autoimmune types of arthritis like RA, DMARDs such as methotrexate are essential. They slow the disease’s progression by targeting the immune system rather than just treating symptoms.
e. Biologic Response Modifiers
Biologics are a newer class of drugs that target specific parts of the immune system. They are often used in combination with DMARDs for people who don’t respond to standard treatment.
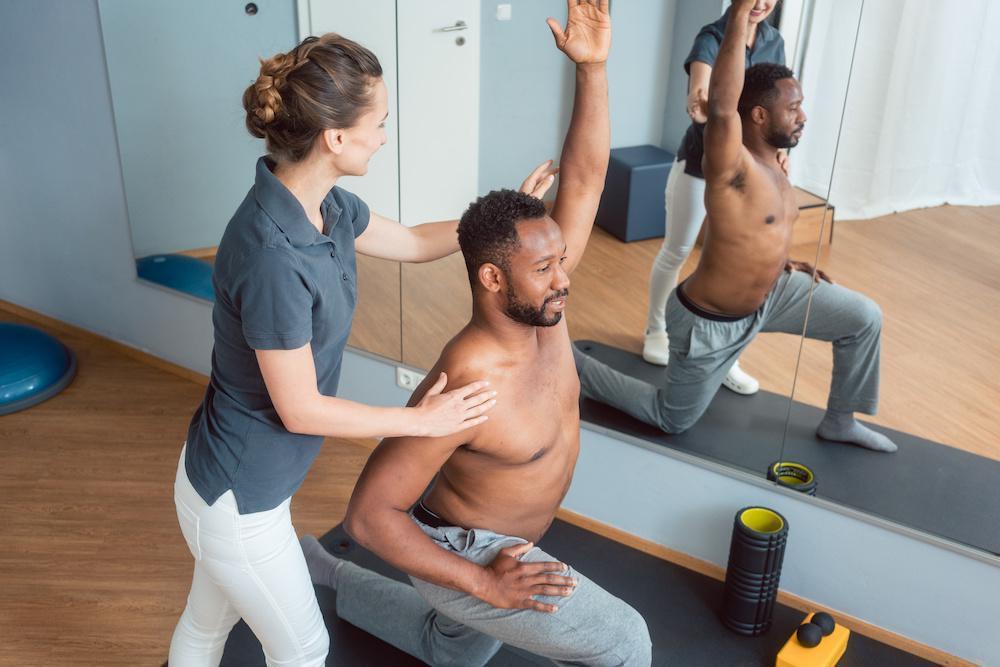

2. Physical Therapy and Exercise
Staying active is one of the most effective ways to manage arthritis pain. While it might seem counterintuitive to move a painful joint, physical activity actually helps keep joints flexible and strengthens the muscles around them.
a. Range-of-Motion Exercises
These exercises help maintain or improve joint flexibility and reduce stiffness. Examples include shoulder rolls, wrist bends, and ankle rotations.
b. Strength Training
Strengthening the muscles surrounding arthritic joints reduces stress on the joints themselves. Resistance bands, light weights, or body-weight exercises can be beneficial.
c. Low-Impact Aerobic Activities
Swimming, cycling, and walking are excellent low-impact exercises that boost cardiovascular health without putting undue strain on the joints.
d. Physical Therapy
A licensed physical therapist can design a custom program tailored to your specific needs and limitations. Therapy may also include modalities like ultrasound or electrical stimulation for pain relief.

3. Diet and Nutrition
There is growing evidence that diet plays a significant role in managing arthritis symptoms. Certain foods can reduce inflammation, while others may trigger flare-ups.
a. Anti-Inflammatory Foods
Incorporate foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids like salmon, flaxseeds, and walnuts. Leafy greens, berries, olive oil, and turmeric also have powerful anti-inflammatory properties.
b. Avoid Processed Foods and Sugars
Processed foods, refined sugars, and trans fats can exacerbate inflammation. Reducing or eliminating these from your diet may help reduce joint pain and stiffness.
c. Maintain a Healthy Weight
Excess weight puts additional stress on weight-bearing joints like the knees and hips. Losing even a few pounds can significantly improve symptoms and mobility.

4. Alternative and Complementary Therapies
Many people find relief from arthritis pain using natural or alternative remedies, especially when used alongside conventional treatments.
a. Acupuncture
This traditional Chinese therapy involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body. Some studies show it can help reduce arthritis pain and improve joint function.
b. Massage Therapy
Regular massage can reduce muscle tension, improve circulation, and enhance range of motion in arthritic joints. It also promotes relaxation and stress relief.
c. Heat and Cold Therapy
Applying heat (warm compresses, heating pads) can reduce stiffness, while cold packs help numb sharp pain and reduce inflammation. Alternating between the two can be especially effective.
d. Supplements
Some supplements may ease arthritis symptoms. Popular choices include:
-
Glucosamine and chondroitin: believed to support cartilage health.
-
Turmeric (curcumin): known for its anti-inflammatory properties.
-
Omega-3 fatty acids: help reduce joint stiffness and pain.
Always consult a healthcare provider before starting any supplement regimen.

5. Assistive Devices and Home Modifications
Making adjustments to your daily environment can reduce strain on joints and make everyday tasks easier.
a. Braces and Supports
Wearing joint supports or braces can provide stability and reduce pain during activity.
b. Canes and Walkers
Mobility aids like canes, walkers, or grab bars can help you move around safely and prevent falls.
c. Ergonomic Tools
Kitchen gadgets, pens, and gardening tools designed with arthritis in mind can ease the strain on hands and wrists.
d. Home Modifications
Installing ramps, stairlifts, or lever-style door handles can enhance independence and safety at home.
6. Mind-Body Techniques
Chronic pain can take a toll not just physically, but mentally and emotionally. Incorporating mental wellness practices can enhance overall treatment effectiveness.
a. Meditation and Mindfulness
Practicing mindfulness meditation can help individuals better cope with chronic pain by reducing stress and improving focus and mood.
b. Yoga and Tai Chi
These gentle practices combine physical movement with breathing and relaxation techniques. They improve flexibility, balance, and mental clarity, all while easing joint discomfort.
c. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
CBT helps patients change negative thought patterns and develop healthy coping strategies, which can be especially beneficial for managing chronic pain.
7. Surgical Options
When conservative treatments fail to provide relief, surgery may be considered, especially in cases of severe joint damage.
a. Joint Replacement (Arthroplasty)
This procedure involves removing the damaged joint and replacing it with an artificial one. Knee and hip replacements are the most common and can dramatically improve quality of life.
b. Joint Fusion (Arthrodesis)
In this surgery, bones are fused together to prevent joint movement. It’s typically used in smaller joints like those in the wrist or ankle.
c. Synovectomy
This involves removing the inflamed joint lining (synovium) and is most often performed in cases of rheumatoid arthritis.

Final Thoughts
Arthritis may not have a one-size-fits-all cure, but the variety of treatment options available means that relief is possible for most people. A holistic approach that combines medication, exercise, diet, alternative therapies, and mental health support often yields the best results. Consulting with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized plan is the first and most important step toward reclaiming mobility and living with less pain.
Remember, the key to managing arthritis is consistency—daily choices in diet, movement, and treatment adherence all add up to make a significant impact over time.